머신러닝 프로그래밍 5주차 응용하기-통계분석1
1. 파이썬통계분석
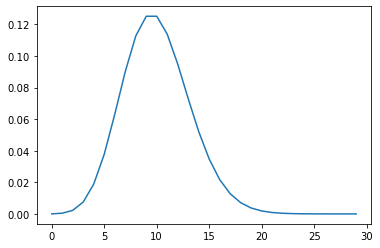
1.1 포아송 분포
포아송 분포는 임의의 사건이 단위 시간당 발생하는 건수가 따르는 확률분포이다. 발생하는 건수의 확률분포이므로, 확률변수가 취할 수 있는 값은{0,1,2,…}가 된다.
예를 들어 어던 사이트에 대한 엑세스를 완전한 임의의 사건으로 간주하면, 단위 시간(한 시간)당 평균 10번 액세스하는 사이트에 대한 한 시간당 엑세스 건수는 Poi(10)을 따른다.
scipy.stats에서 포아송 분포는 poisson 함수로 다음과 같이 구할 수 있다.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import scipy.stats as stats
lamb = 10
x = 3
rv = stats.poisson(lamb)
rv.pmf(x) # P (X = 3)
0.007566654960414144
rv.mean()
10.0
rv.var() #분산
10.0
lamb = 10
rv = stats.poisson(lamb)
x = np.arange(0,30)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.plot(x, rv.pmf(x))
plt.show()
1.2 y = ax +b 그래프
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
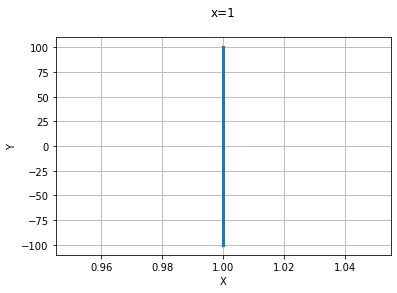
x =1 그래프
xs = np.linspace(1,1,200+1)
xs
array([1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.])
ys = np.linspace(-100,100,200+1)
ys
array([-100., -99., -98., -97., -96., -95., -94., -93., -92.,
-91., -90., -89., -88., -87., -86., -85., -84., -83.,
-82., -81., -80., -79., -78., -77., -76., -75., -74.,
-73., -72., -71., -70., -69., -68., -67., -66., -65.,
-64., -63., -62., -61., -60., -59., -58., -57., -56.,
-55., -54., -53., -52., -51., -50., -49., -48., -47.,
-46., -45., -44., -43., -42., -41., -40., -39., -38.,
-37., -36., -35., -34., -33., -32., -31., -30., -29.,
-28., -27., -26., -25., -24., -23., -22., -21., -20.,
-19., -18., -17., -16., -15., -14., -13., -12., -11.,
-10., -9., -8., -7., -6., -5., -4., -3., -2.,
-1., 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7.,
8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13., 14., 15., 16.,
17., 18., 19., 20., 21., 22., 23., 24., 25.,
26., 27., 28., 29., 30., 31., 32., 33., 34.,
35., 36., 37., 38., 39., 40., 41., 42., 43.,
44., 45., 46., 47., 48., 49., 50., 51., 52.,
53., 54., 55., 56., 57., 58., 59., 60., 61.,
62., 63., 64., 65., 66., 67., 68., 69., 70.,
71., 72., 73., 74., 75., 76., 77., 78., 79.,
80., 81., 82., 83., 84., 85., 86., 87., 88.,
89., 90., 91., 92., 93., 94., 95., 96., 97.,
98., 99., 100.])
plt.grid(True)
plt.title('x=1\n')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.plot(xs,ys,linewidth=3)
plt.show()
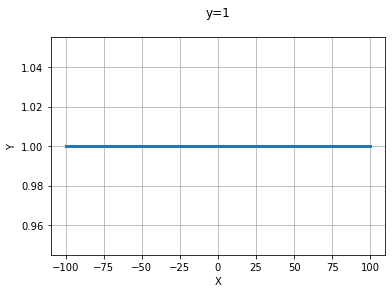
y =1 그래프
xs = np.linspace(-100,100,200+1)
xs
array([-100., -99., -98., -97., -96., -95., -94., -93., -92.,
-91., -90., -89., -88., -87., -86., -85., -84., -83.,
-82., -81., -80., -79., -78., -77., -76., -75., -74.,
-73., -72., -71., -70., -69., -68., -67., -66., -65.,
-64., -63., -62., -61., -60., -59., -58., -57., -56.,
-55., -54., -53., -52., -51., -50., -49., -48., -47.,
-46., -45., -44., -43., -42., -41., -40., -39., -38.,
-37., -36., -35., -34., -33., -32., -31., -30., -29.,
-28., -27., -26., -25., -24., -23., -22., -21., -20.,
-19., -18., -17., -16., -15., -14., -13., -12., -11.,
-10., -9., -8., -7., -6., -5., -4., -3., -2.,
-1., 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7.,
8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13., 14., 15., 16.,
17., 18., 19., 20., 21., 22., 23., 24., 25.,
26., 27., 28., 29., 30., 31., 32., 33., 34.,
35., 36., 37., 38., 39., 40., 41., 42., 43.,
44., 45., 46., 47., 48., 49., 50., 51., 52.,
53., 54., 55., 56., 57., 58., 59., 60., 61.,
62., 63., 64., 65., 66., 67., 68., 69., 70.,
71., 72., 73., 74., 75., 76., 77., 78., 79.,
80., 81., 82., 83., 84., 85., 86., 87., 88.,
89., 90., 91., 92., 93., 94., 95., 96., 97.,
98., 99., 100.])
ys = np.linspace(1,1,200+1)
ys
array([1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.])
plt.grid(True)
plt.title('y=1\n')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.plot(xs,ys,linewidth=3)
plt.show()
y=1 그래프 f(x)
y = f(x) 의 형태로 코딩
xs = np.linspace(-100,100,200+1)
xs
array([-100., -99., -98., -97., -96., -95., -94., -93., -92.,
-91., -90., -89., -88., -87., -86., -85., -84., -83.,
-82., -81., -80., -79., -78., -77., -76., -75., -74.,
-73., -72., -71., -70., -69., -68., -67., -66., -65.,
-64., -63., -62., -61., -60., -59., -58., -57., -56.,
-55., -54., -53., -52., -51., -50., -49., -48., -47.,
-46., -45., -44., -43., -42., -41., -40., -39., -38.,
-37., -36., -35., -34., -33., -32., -31., -30., -29.,
-28., -27., -26., -25., -24., -23., -22., -21., -20.,
-19., -18., -17., -16., -15., -14., -13., -12., -11.,
-10., -9., -8., -7., -6., -5., -4., -3., -2.,
-1., 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7.,
8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13., 14., 15., 16.,
17., 18., 19., 20., 21., 22., 23., 24., 25.,
26., 27., 28., 29., 30., 31., 32., 33., 34.,
35., 36., 37., 38., 39., 40., 41., 42., 43.,
44., 45., 46., 47., 48., 49., 50., 51., 52.,
53., 54., 55., 56., 57., 58., 59., 60., 61.,
62., 63., 64., 65., 66., 67., 68., 69., 70.,
71., 72., 73., 74., 75., 76., 77., 78., 79.,
80., 81., 82., 83., 84., 85., 86., 87., 88.,
89., 90., 91., 92., 93., 94., 95., 96., 97.,
98., 99., 100.])
def f_y1(x):
return np.linspace(1,1,len(x))
ys = f_y1(xs)
ys
array([1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.])
plt.grid(True)
plt.title('y=1\n')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.plot(xs,ys,linewidth=3)
plt.show()
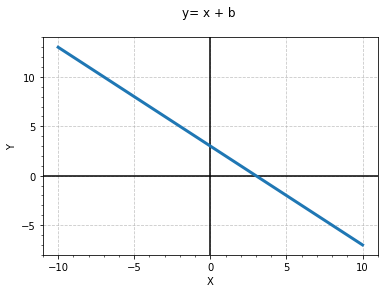
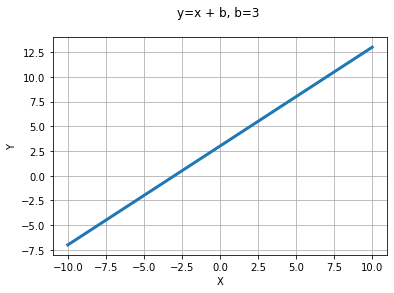
y = x + b 그래프
xs = np.linspace(-10,10,20+1)
xs
array([-10., -9., -8., -7., -6., -5., -4., -3., -2., -1., 0.,
1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9., 10.])
def f_x_plus_b(x,b):
return x + b
b =3
ys = f_x_plus_b(xs, b)
ys
array([-7., -6., -5., -4., -3., -2., -1., 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5.,
6., 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13.])
plt.grid(True)
plt.title('y=x + b, b=3 \n')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.plot(xs,ys,linewidth=3)
plt.show()
# 보기 편하게 그래프 수정
plt.grid(True, linestyle='--')
plt.title('y= x + b \n')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.axhline(0, color='black')#y=0 라인
plt.axvline(0, color='black')#x=0 라인
plt.plot(xs,ys,linewidth=3)
plt.show()
# 보기 편하게 그래프 수정 2
ticks_major = np.arange(-20,20,5)
print(ticks_major)
ticks_minor = np.arange(-20,20,1)
print(ticks_minor)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
ax.set_xticks(ticks_major)
ax.set_xticks(ticks_minor, minor=True)
ax.set_yticks(ticks_major)
ax.set_yticks(ticks_minor, minor=True)
ax.grid(which='both')
ax.grid(which='minor', alpha=0.2)
ax.grid(which='major', alpha=0.7)
plt.grid(True, linestyle='--')
plt.title('y= x + b \n')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.axhline(0, color='black')#y=0 라인
plt.axvline(0, color='black')#x=0 라인
plt.plot(xs,ys,linewidth=3)
plt.show()
[-20 -15 -10 -5 0 5 10 15]
[-20 -19 -18 -17 -16 -15 -14 -13 -12 -11 -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3
-2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
16 17 18 19]
# 보기 편하게 그래프 수정 3
def my_plot_default(xs, ys,title):
ticks_major = np.arange(-20,20,5)
ticks_minor = np.arange(-20,20,1)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)
ax.set_xticks(ticks_major)
ax.set_xticks(ticks_minor, minor=True)
ax.set_yticks(ticks_major)
ax.set_yticks(ticks_minor, minor=True)
ax.grid(which='both')
ax.grid(which='minor', alpha=0.2)
ax.grid(which='major', alpha=0.7)
plt.grid(True, linestyle='--')
plt.title('y= x + b \n')
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.axhline(0, color='black')#y=0 라인
plt.axvline(0, color='black')#x=0 라인
plt.plot(xs,ys,linewidth=3)
plt.show()
xs = np.linspace(-10,10,20+1)
b =3
ys = f_x_plus_b(xs,b)
my_plot_default(xs, ys, 'y= x+b')
y =ax + b 그래프
def f_ax_plus_b(x,a,b):
return a * x +b
xs = np.linspace(-10,10,20+1)
a = -1
b = 3
ys = f_ax_plus_b(xs,a,b)
my_plot_default(xs, ys,'y=x+b')